Webhooks
Webhooks provide integration capabilities by sending signed HTTPs requests to external APIs when campaign events occur.
Overview
The webhook overview shows you all webhooks created and available for use in campaigns.
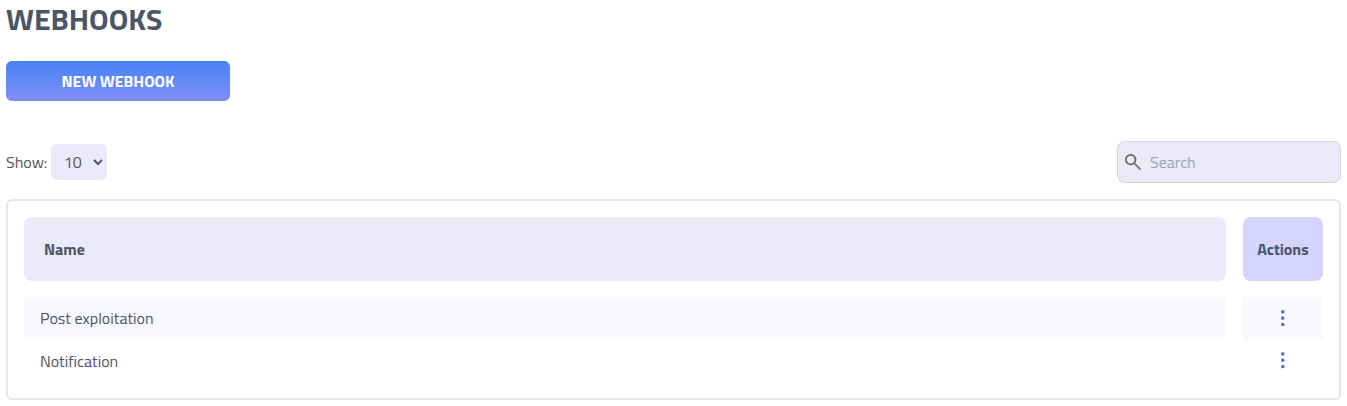
Click on the name of a webhook to edit it.
Create new webhook
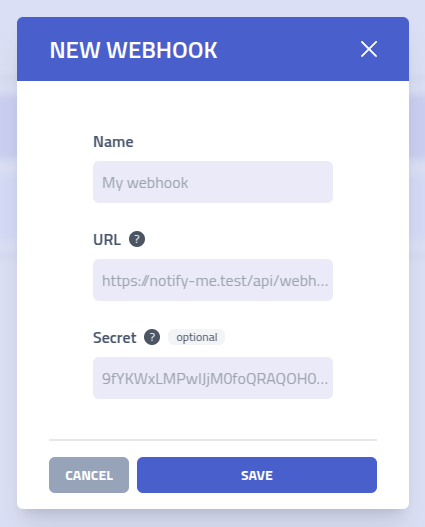
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Webhook Name | Identifier for this webhook endpoint configuration |
| Target URL | HTTPS endpoint URL where webhook requests will be sent for event processing |
| Secret Key | Secret for HMAC-SHA256 signature generation, enabling verification of webhook authenticity |
Request Format
Webhook requests include authentication headers and a JSON body:
Accept-Encoding: gzip
User-Agent: Go-http-client
Content-Length: 142
Content-Type: application/json
X-Signature: 3ec2d0d777495b4410331a8e22de309e393761ed2e16f4271577e812ffaf26e3
{
"time":"2025-03-30T12:13:00.026471259Z",
"campaignName":"Example",
"email":"[email protected]",
"event":"campaign_recipient_message_sent"
}
Event types
Webhooks are triggered for the following campaign events:
| Event Name | Trigger Description |
|---|---|
campaign_recipient_message_sent | Email successfully delivered to recipient's mailbox |
campaign_recipient_message_read | Recipient opened email (read confirmation received) |
campaign_recipient_before_page_visited | Pre-landing page accessed by recipient |
campaign_recipient_page_visited | Main phishing landing page accessed by recipient |
campaign_recipient_after_page_visited | Post-landing page accessed by recipient |
campaign_recipient_submitted_data | Recipient submitted information through phishing page forms |
Verifying webhooks
Webhook security is implemented with HMAC-SHA256 signature verification, ensuring that incoming webhook requests originate from Phishing Club and have not been tampered.
When configuring a webhook with a secret key, each request includes an X-Signature
header containing an HMAC-SHA256 signature of the request body. Your application can verify this
signature to confirm the webhook's authenticity.
Verification implementation
The X-Signature header contains the request body signed with HMAC-SHA256 using your
configured secret key. Here's an example implementation in Go for verifying webhook signatures:
bodyBytes, err := io.ReadAll(body)
if err != nil {
log.Println("failed to read body for HMAC calculation:", err)
http.Error(w, "failed to read body", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
h := hmac.New(sha256.New, []byte("YOUR_SECRET_KEY_HERE"))
h.Write(bodyBytes)
calculatedHMAC := hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
// Get the signature from the header
signature := req.Header.Get("x-signature")
if calculatedHMAC != signature {
http.Error(w, "invalid HMAC signature", http.StatusForbidden)
return
}
Note: When no secret key is configured, the X-Signature header
will contain the value UNSIGNED, indicating that signature verification is not
available for that webhook.

